Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
The most abundant atoms in living organisms are:
a. | carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. | c. | carbon, oxygen and
nitrogen. | b. | sulfur and nitrogen. | d. | oxygen and phosphorus. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Figure 1 shows a chemical reaction. In this chemical reaction, glucose
is:
a. | a product. | c. | a form of energy. | b. | a reactant. | d. | a lipid. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Figure 1 shows what chemical reaction?
a. | Cellular Respiration | c. | Krebs Cycle | b. | Photosynthesis | d. | Symbiosis |
|
|
|
4.
|
The following diagram represents the following EXCEPT: 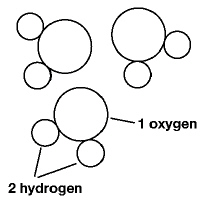 a. | water. | c. | a compound. | b. | a molecule. | d. | an element. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which equation below represents photosynthesis?
a. | CO2 + H2O ------>
C6H12O6 + O2 | b. | C6H12O6 + O2 ------>
CO2 + H2O |
|
|
|
6.
|
A ____ is a group of two or more atoms joined together chemically.
a. | cell | b. | solution | c. | light
ray | d. | molecule |
|
|
|
7.
|
The process of rearranging atoms in one substance into a new substance is called
a:
a. | production. | b. | chemical reaction. | c. | compound. | d. | solution. |
|
|
|
8.
|
A(n) ____ is the simplest form of matter.
a. | cell | b. | element | c. | molecule | d. | compound |
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | atom | f. | photosynthesis | b. | compound | g. | pigment | c. | chemical
reaction | h. | cellular
respiration | d. | element | i. | chlorophyll | e. | molecule |
|
|
|
9.
|
a process that rearranges the atoms of one or more substances into one or more
new substances
|
|
|
10.
|
a substance that contains two or more different elements that are chemically
joined
|
|
|
11.
|
the smallest particle of an element that keeps the chemical identity of that
element.
|
|
|
12.
|
a process where plants use the energy of sunlight to produce
carbohydrates
|
|
|
13.
|
a molecule that absorbs some colors of light and reflects others
|
|
|
14.
|
a group of two or more atoms joined together chemically
|
|
|
15.
|
the main pigment used in photosynthesis that absorbs blue and red light and
reflects green light.
|
|
|
16.
|
the simplest form of matter
|
|
|
17.
|
the process in which the chemical bonds of energy-rich molecules are converted
into a form of energy that cells can use.
|